Table of Contents
ToggleMaster Your Finances: A Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating EMIs
I. Understanding EMIs Calculation: A Brief Introduction
In this section, we will provide a basic understanding of what Equated Monthly Instalments (EMIs) are and their significance in financial planning.
1.1 What are EMIs?
Is, or Equated Monthly Instalments, are fixed monthly payments made towards repaying a loan. They consist of two components: the principal amount and the interest charged on the loan. EMIs are a common method of loan repayment and play a crucial role in managing your finances.
1.2 Components of an EMI Calculation
To understand how EMIs are calculated, it’s important to be familiar with the components involved:
- Principal amount: This refers to the borrowed amount, the total sum that is being financed through the loan.
- Interest rate: The interest rate is the percentage at which the lender charges interest on the loan amount.
- Loan term: The loan term is the duration within which the loan is to be repaid, typically expressed in months or years.
Understanding these components is essential for calculating EMIs accurately.
1.3 Importance of EMI Calculation
Knowing your EMIs beforehand offers several benefits:
- Financial planning: Calculating EMIs helps you plan your monthly budget and manage your finances effectively. It enables you to determine whether the loan is affordable and fits your financial goals.
- Budgeting: EMIs have a significant impact on your monthly budget. By calculating your EMIs, you can allocate funds accordingly, ensuring that you meet your repayment obligations without compromising on other essential expenses.
II. EMI Calculation Methodologies
This section will cover different methods used for calculating EMIs. Each method will be explained in detail, along with their advantages and limitations.
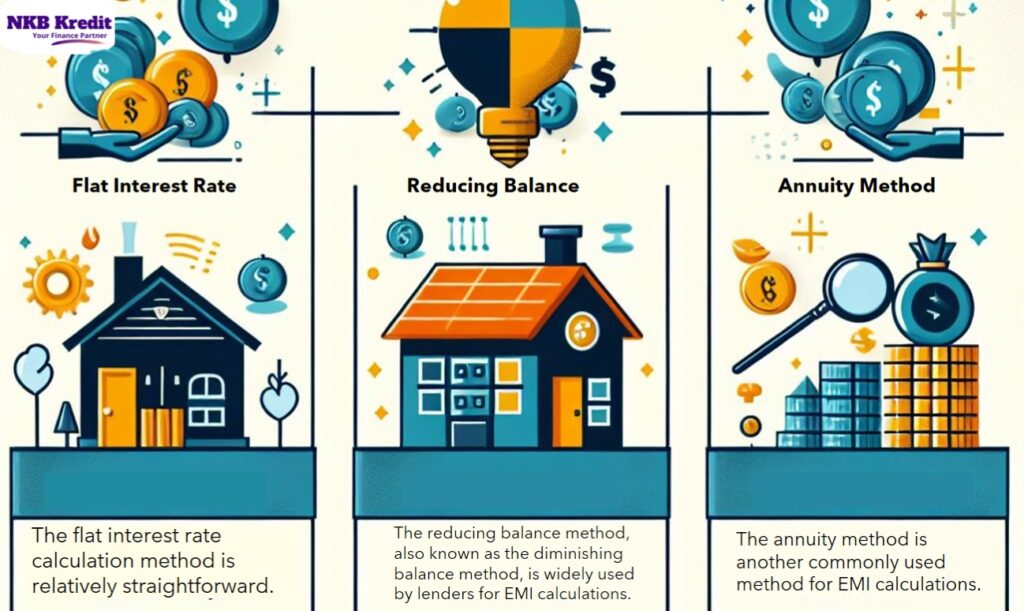
2.1 Flat Interest Rate Method
The flat interest rate calculation method is relatively straightforward. It considers the original loan amount and applies a fixed percentage as interest throughout the loan tenure. However, the interest is not recalculated based on the outstanding principal balance.
To calculate the EMI using the flat interest rate method, you can use the following formula:
EMI = (Principal + (Principal * Interest Rate * Loan Term)) / Loan Term
While the flat interest rate method is simple to understand and calculate, it may not provide an accurate representation of the true cost of borrowing over time.
2.2 Reducing Balance Method
The reducing balance method, also known as the diminishing balance method, is widely used by lenders for EMI calculations. It takes into account the outstanding principal balance when calculating the interest.
To calculate the EMI using the reducing balance method, follow these steps:
- Calculate the monthly interest rate by dividing the annual interest rate by 12.
- Determine the loan tenure in months.
- Use the following formula to calculate the EMI:
EMI = (Principal * Monthly Interest Rate * (1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^Loan Term) / ((1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^Loan Term – 1)
The reducing balance method provides a more accurate representation of the total interest paid over the loan tenure, making it the preferred choice for most borrowers.
2.3 Annuity Method
The annuity method is another commonly used method for EMI calculations. It considers the loan as a series of equal periodic payments, including both principal and interest. The interest component decreases over time, while the principal component increases.
To calculate EMIs using the annuity method, follow these steps:
- Calculate the monthly interest rate by dividing the annual interest rate by 12.
- Determine the loan term in months.
- Use the following formula to calculate the EMI:
EMI = [Principal * Monthly Interest Rate * (1 + Monthly Interest Rate) ^Loan Term] / [(1 + Monthly Interest Rate) ^Loan Term – 1]
The annuity method provides a balance between the simplicity of flat interest rate calculations and the accuracy of reducing balance calculations.
2.4 Online EMI Calculation and Applications
Using online EMI calculation calculators simplifies the calculation process and provides accurate results. These calculators are widely available and can be accessed through various websites or mobile applications.
The benefits of using online EMI calculation include:
- Convenience: Online calculators provide a quick and hassle-free way to calculate your EMIs.
- Accuracy: These calculators use advanced algorithms to ensure accurate calculations, taking into account different components such as interest rate, loan term, and principal amount.
- Comparison: Many online calculators allow you to compare EMIs for different loan amounts, interest rates, and tenures, helping you choose the most suitable option.
Recommended online EMI calculation applications include Bankrate, EMI calculation Calculator by Money Control, and ICICI Bank EMI calculation Calculator.
EMI Calculator: https://www.nkbkredit.com/emi-calculator/
III. Factors Affecting EMI Calculation
This section will discuss various factors that can influence the calculation of EMIs, helping readers understand how different elements impact their monthly instalment amounts
3.1 Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the EMI amount. Fluctuations in interest rates can significantly affect your monthly instalment. It is essential to consider the following when choosing fixed or floating interest rates:
- Fixed interest rates: With fixed interest rates, your EMI remains constant throughout the loan tenure, providing stability and predictability in your monthly budget.
- Floating interest rates: Floating interest rates, also known as variable interest rates, fluctuate with market conditions. While they may start lower than fixed rates, they can increase in the future, causing changes in your EMI.
Lenders often base the interest rate offered on your credit score, so maintaining a good credit score can help you secure a favourable interest rate.
3.2 Loan Tenure
The loan tenure, or the duration for which you repay the loan, has a direct impact on the EMI amount. Consider the following when choosing the loan tenure:
- Longer tenure: Opting for a longer tenure reduces the EMI amount, making it more manageable in the short term. However, it also increases the total interest paid over the loan duration.
- Shorter tenure: Choosing a shorter tenure increases the EMI amount but reduces the overall interest paid. This option is suitable if you can comfortably afford the higher EMIs.
Additionally, you should be aware that prepayment or part-payment of the loan can impact the loan tenure. By making extra payments, you can shorten the loan tenure and reduce the total interest paid.
Bonus content: A Comprehensive Guide to Mortgage Loans for Businesses: 5 Essential Things You Need to Know
3.3 Loan Amount and Down Payment
The principal loan amount has a direct impact on the EMI. Here’s what you need to know:
- Higher loan amount: A higher loan amount translates to higher EMIs. It’s important to consider your income and expenses to ensure that the EMI is affordable.
- Down payment: A down payment refers to the initial amount paid towards the loan from your own funds. A higher down payment reduces the loan amount, thereby decreasing the EMI.
Carefully evaluating your financial situation and opting for an appropriate loan amount and down payment can help you manage your EMIs effectively.

IV. EMI Amortization Schedule: Tracking Your Loan Repayment
This section will delve into the concept of EMI amortization schedules and their significance in tracking the repayment progress of your loan.
4.1 Understanding Amortization
Amortization is the process of gradually reducing a debt over time through regular payments. It helps borrowers understand how their EMIs are allocated towards the principal and interest components.
The amortization process creates an EMI amortization schedule that details the payment distribution over the loan tenure.
4.2 EMI Amortization Schedule Calculation
To calculate the EMI amortization schedule, follow these steps:
- Begin by calculating the EMI amount using one of the EMI calculation methods discussed earlier.
- Determine the loan tenure in months.
- Use the EMI, loan tenure, and interest rate to create a month-by-month breakdown of principal and interest components.
- Update the outstanding principal balance based on the EMI payments made each month.
- Repeat the process until the entire loan is repaid.
The EMI amortization schedule provides valuable insights into your loan repayment progress, helping you plan future payments and make informed financial decisions.
4.3 Managing EMI Changes Over Time
It’s important to note that EMIs can change over time due to fluctuations in interest rates or changes in loan terms. Here are some strategies for managing such changes:
- Refinancing: If interest rates decrease significantly, you may consider refinancing your loan to secure a lower interest rate, which can result in reduced EMIs.
- Loan modification: Contact your lender to discuss the possibility of modifying the loan terms if you anticipate difficulty in meeting the current EMIs.
- Reviewing the schedule: Regularly reviewing your EMI amortization schedule can help you anticipate any changes in EMIs and proactively manage them.
Understanding and tracking your EMI amortization schedule empowers you to make informed decisions regarding your loan repayment.
V. SUMMARY
5.1 Summary of Key Points
To summarize, calculating your EMIs is crucial for effective financial planning. By understanding the components involved, utilizing different calculation methods, considering various factors, and tracking your EMI with an amortization schedule, you can manage your loan efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1: Can I change my EMI amount after the loan approval?
While it is generally challenging to change your EMI amount after loan approval, it is worth contacting your lender to discuss any financial difficulties or the possibility of modifying the loan terms. However, it is essential to carefully consider the impact of such modifications on your loan tenure and total interest paid.
2: Is it better to choose a longer or shorter loan tenure?
The choice between a longer or shorter loan tenure depends on your financial situation and goals. A longer tenure results in lower EMIs but higher overall interest paid, while a shorter tenure translates to higher EMIs but reduced interest. Consider your repayment capacity, financial goals, and other factors to determine which option aligns with your needs.
3: How often should I review my EMI amortization schedule?
It is advisable to review your EMI amortization schedule at regular intervals, especially when interest rates change, you consider refinancing, or you anticipate changes in your financial situation. By monitoring your schedule, you can stay informed about the progress of your loan repayment and make well-informed decisions.
CONCLUSION

In conclusion, calculating your EMIs is a crucial step in financial planning. By understanding the components, utilizing different calculation methods, considering various factors, tracking your EMI with an amortization schedule, and reviewing your progress, you can effectively manage your loan and achieve your financial goals.
Remember to use online EMI calculation calculators for accurate and convenient calculations. Take advantage of the resources available and stay proactive in managing your EMIs for a smoother loan repayment journey.
